Narayan gopal collection
0
Song: Aajai Ra Rati
Artist: Narayan Gopal
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download here
Artist: Narayan Gopal
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download here
Song: Malai Chhodi Mero Chhaya
Artist: Narayan Gopal
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download here
Artist: Narayan Gopal
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download here
Song: Mandir Ma Chha Ki
Artist: Narayan Gopal
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download here
Song: Timro Jasto Mutu
Artist: Narayan Gopal
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.comDownload from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download here
Song: Yeti Chokho Yeti Mitho
Artist: Narayan Gopal
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download here
Song: Chori Ko Janma
Artist: Narayan Gopal
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download here
Feri Bhetaula; Hami Agyani; Jaga Jaga; Malai Pani Hidna Lai; Sunideu Sunideu; Udayo Rail Lai Le
0
Song: Malai Pani Hidna Lai
Artist: Namaste Band
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download here
Song: Sunideu Sunideu
Artist: Namaste Band
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download here
Song: Udayo Rail Lai Le
Artist: Namaste Band
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download here
hiu bhanda chiso
0
Song: Hiu Bhanda Chiso Ho
Artist: Danny Denzogpa
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download here
Hiu Bhanda Chiso Ho; Rato Rani; Suna Katha
0
Song: Hiu Bhanda Chiso Ho
Artist: Danny Denzogpa
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download here
Song: Suna Katha
Artist: Danny Denzogpa
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download here
Anautho tyatha, timro mero, thula thula mahal hoina, zindagi ko ke bharosa, man manai, bistrai chayo , bhetera chutnu bhanda , sahanchan sabaile , papi rahechha, lahure lai ...
0
Song: Anautho Byatha
Artist: Karna Das
Song: Timro Mero
Artist: Karna Das
Song: Thula Thula Mahal Hoina
Artist: Karna Das
Song: Zindagi Ko Ke Bharosa
Artist: Karna Das
Song: Man Manai
Artist: Karna Das
Song: Bistarai Chayo
Artist: Karna Das
Song: Bhetera Chutnu Bhanda
Artist: Karna Das
Song: Sahanchan Sabaile
Artist: Karna Das
Song: Papi Rahichha
Artist: Karna Das
Song: Lahure Lai
Artist: Karna Das
Download from www.your1click.blogspot.com
Download here
kusume rumal all songs
0Song: Bhooli Gaye Samjhana Lai Kusume Rumal
0
Type : MOVIE SONG
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Song: Bhooli Gaye Samjhana Lai Kusume Rumal
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Song: Bhooli Gaye Samjhana Lai Kusume Rumal
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Reli Khola Bagara
0
Type : MOVIE SONG
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Reli Khola Bagara
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Reli Khola Bagara
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Kusume rumal movie song's Instrumental
0
Type : MOVIE SONG
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Instrumental
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Instrumental
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Suna Bhan Na Juna Hera Na
0
Type : MOVIE SONG
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Suna Bhan Na Juna Hera Na
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Suna Bhan Na Juna Hera Na
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Timi Nabhaye Zindagi Kaanda Sari Cha
0
Type : MOVIE SONG
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Timi Nabhaye Zindagi Kaanda Sari Cha
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Timi Nabhaye Zindagi Kaanda Sari Cha
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Mayako Barima (Solo)
0
Type : MOVIE SONG
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Mayako Barima (Solo)
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Mayako Barima (Solo)
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Kaichimar Sari Satanko Pari
0
Type : MOVIE SONG
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Kaichimar Sari Satanko Pari
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Kaichimar Sari Satanko Pari
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Mayako Barima (DUET)
0
Type : MOVIE SONG
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Mayako Barima(Duet)
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Mayako Barima(Duet)
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Mayako Barima (Instrumental)
0
Type : MOVIE SONG
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Mayako Barima (Instrumental)
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Aritst : Kusume Rumal
Song : Mayako Barima (Instrumental)
Download from www.your1clicksongs.blogspot.com
Download this
Lie Detector Circuit Explanation -with video
0

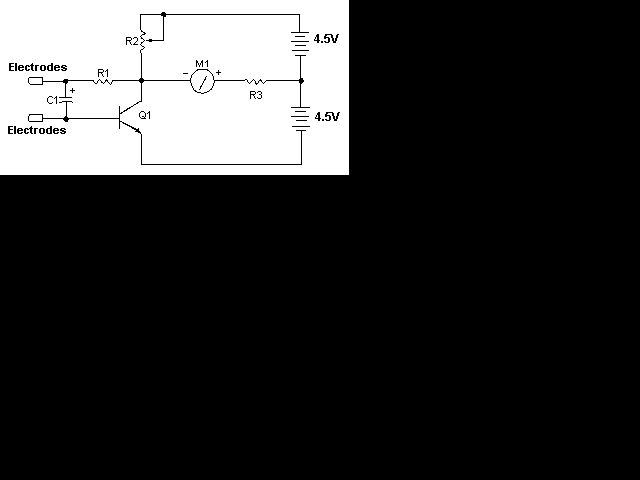
This circuit is a basic two transistor direct-coupled oscillator with a frequency determined by the capacitor and the resistance of the skin.
According to the theory; the lie detector, also called "polygraph"1, can detect changes in the resistance of the human body. Is supposed that when someone lies, the resistance of the body is lower because the sweat and other factors. So the change in the frequency of the sound will indicate it.
Lie Detector Electronic Kit and Circuit Explanation - Voltage ...
0
A person holding the probe wires will change the voltage at the upper probe wire depending on their skin resistance. The skin resistance is in parallel with R2 and, because it is likely to be similar to or smaller than R2, the voltage at the probe wire will fall as skin resistance falls.
The circuit diagram of the Lie Detector is shown above. It consists of three transistors (TR1 to TR3), a capacitor (C1), two lights or LEDs (L1 & L2), five resistors (R1 to R5), and a variable resistor (VR1). This circuit is based on the fact that a person's skin resistance changes when they sweat (sweating because they're lying). Dry skin has a resistance of about 1 million ohms, whereas the resistance of moist skin is reduced by a factor of ten or more. Resistors R1 and R2 form a voltage divider.They have resistances of 1 000 000 ohms (1 mega ohms) and, because their values are equal, the voltage at the upper probe wire is half the battery voltage (about 4.5 volts).
A person holding the probe wires will change the voltage at the upper probe wire depending on their skin resistance. The skin resistance is in parallel with R2 and, because it is likely to be similar to or smaller than R2, the voltage at the probe wire will fall as skin resistance falls.
Capacitor C1 functions as a smoothing capacitor and removes the 50Hz induced mains hum that is found on a person's body.
TR1 and R3 form a buffer circuit (called an emitter-follower). The voltage at the emitter of TR1 follows the voltage at the probe wire and is now able to drive transistor TR2.
Transistors TR1 and TR2 act as a voltage comparator. If the voltage at the base of TR2 is higher than at the base of TR3 then the green LED (L1) will come on. If the reverse is true then the red LED (L2) will light.
To test the Lie Detector hold the probe wires. Adjust VR1 until the green LED is just on and the red LED is just off. This is the point at which the voltage at the base of TR2 is just greater than at the base of TR3. Now use moist fingers to hold the probes. This lowers the skin resistance and causes the voltage at the base of TR2 to fall. The voltage at the base of TR3 is now greater and the red LED comes on.
any remote support, you can use any load in out put terminels and pc aslo
0
Click for PDF file
PC Software
The PC software used is PC Remote Control. As it does not require the use of the RX line on the USART. It is better for experimentation as it lets you generate TX data only and it does not check whether the microcontroller is active by querying the microcontroller (generating data to the Rx port of the microcontroller) i.e. you only have to generate TX data and not worry about RX data so it's easier. Some control programs won't proceed unless the microcontroller gives the correct response.
What is IR how its work ???
0
Ok now I'm not going to start from ground zero and work up. This is a basic discussion of IR and how it is frequently used in robotics. IR is infrared light or light that is outside the visible light spectrum, in other words the naked eye cannot see it. IR light does not obey all the same properties as visible light. IR can pass through certain types/colors of plastic and some other materials, it is VERY easily reflected off most objects, and it is very prevalent in today's electronics. For instance, the remote for your TV/VCR probably uses IR control. The remote flashes an Infrared Light Emitting Diode at a certain rate a certain number of times and an Infrared receiver detects this and takes appropriate actions based on the transmission. Most IR applications, including TV remotes, operate at 40 KHz. That is to say, the IR LED is turned on and off 40,000 times per second. This is the frequency that the device operates at. Now if we turn this 40 KHz signal off and on we have essentially made a digital device. Much like a computer we are sending either a 1 or a 0 (1=high/on 0=low/off). Now we can transmit data by modulating (turning on and off) that 40 KHz signal.
Why use 40 KHz? Why not just on and off? Ambient light contains some IR and the sun outputs a lot of IR so we need a way to 'code' our signal to make sure it doesn't get lost in all the other IR light bouncing around out there. For the same reason we have different radio channels, it would be pretty hard to understand even one channel if we had to listen to them all at once. The only reason I have ever found as to why we use 40 KHz is because the first Ultrasonic TV remotes used that same frequency, IR just adopted it to keep things consistent I guess.
So what is the simplest task we could accomplish with IR on our robot? We can use this information to create object detection and avoidance for out bots. The great thing about IR is the bot can detect an object without touching it. We create a 40 KHz circuit using a 555 timer circuit and connect it's output to an infrared LED. On the receiver side we go and buy an IR receiver module for about $3 from Radio Shack or similar store. The receiver module automatically filters the 40 KHz and leaves us with either high output (5v) or low (Gnd). To make sure the receiver doesn't 'float' we tie a 10k ohm resistor from Gnd to the output of the receiver, this is just to make the signal clear. Now we hook up the output into our Basic Stamp or PIC or whatever is controlling our robot and we now have object detection ( object ahead=reflection=high output from receiver). Point the LED to face the ground and we now have drop off detection ( drop off=no reflection=low output from receiver).
What happens if we take two of these circuits, one for object detection and one for drop off detection and put them on one bot?? Won't the transmitted signals bounce around and fool both receiver modules?? Yes, here's how you get around it. Instead of just turning our 40 KHz 555 timers on and leaving them on, turn on one and then monitor the value of the corresponding receiver then turn it off. Do this for each TX/RX pair you have, the microcontroller should be fast enough to get at least 5 or more samples per second. Not too shabby.
A basic IR object detection circuit can be built for under $7 and from only 8 parts - 555 timer, 3 resistors, 1 capacitor, 1 IR LED, and 1 IR receiver module. The 555 uses 2 resistors and the capacitor to make the 40 KHz signal and then outputs to the IR LED ( I use a resistor in line with the IR LED to limit current draw, the resistor size will vary with IR LED, use ohms law to determine max current draw). The receiver then has it's output tied to ground with the last resistor and Viola, your finished. You can also use a 74HCT14 to produce the 40 KHz, it uses less parts and it is more stable too. These circuits will appear on the schematics page soon.
Now own to IR remote controls. Your garden variety IR remote for TV, VCR, Cable box, etc. uses the same 40 KHz modulation we have talked about already. Here is how the actual signal breaks down (for Sony type remotes).
There are really only three different ways that manufacturers choose to code these signals. This coding is usually based on varying the length of pulses, varying the length of spaces between pulses or altering the order between spaces or pulses.
This coding holds information such as the address to the machine that is using the remote and the command that the machine must follow. The address is very important because without it the signal would be processed by another IR receiver in the area.
When a button on a remote is pushed it sends a string of signals. The first piece of information in the string is called the Header. The Header usually contains a burst of highs that alerts all the IR receivers in the area to the string of data being sent. Following the burst of highs is the address to the specific machine to receive the next piece of data, the command. As long as the button is held down (depressed) the command will continue to repeat over and over. When the button is released a string of code called the stop is transmitted. As you may have guessed it the stop tells the machine to stop its executing the command.
Performance The Sony remote control is based on the Pulse-Coded signal coding scheme. It is a 12-bit signal sent on a 40 kHz IR wave. The signal is started by a header which is a pulse for 4T and then spacing for T where T is 550 us. Following the header is the address and the command which consists of logical zeros and logical ones. Logical ones are represented by a 2T pulse followed by a T space. Logical zeros are represented by a T pulse followed by a T space. The space between transmissions is 25 ms. As long as the but
remote transmitter by using 555
0
The first project I posted to Robot Room involved a 74HC00 NAND infrared oscillator. Nine months have passed and I'd learned a lot. The power usage of my original NAND oscillator can be reduced without any loss of drive or functionality
- Swap in a Toshiba 74HC00A NAND
- Switch the 10-kilohm pull-up resistor for 100 kilohms
- Eliminate a whole inverting buffer gate by switching the 2N2222 NPN transistor driver to a 2N2907 PNP transistor driver.
I wrote this web page in March 2001. The circuit presented here is perfectly good for builder the 38 kHz emitter. However, because I get a lot of questions about infrared sensors and detectors, I decided to dedicate two chapters (11 and 12) of my second book, Intermediate Robot Building, to the subject. Therefore, if you'd like more information, including an improved schematic with receivers and detectors, pick up a copy of the book.
Usage
The oscillator will be used to generate a square wave at a desired frequency. The wave is fed into a transistor that drives an infrared LED on and off very rapidly. Because the emissions are infrared and very fast, neither is visible to the human eye. Inexpensive infrared receiver chips are available at 36 kHz, 38 kHz, and 40 kHz. The receivers are sensitive to oscillations several kilohertz to either side, although reception distance improves with a better signal to start with. If used for object detection, the signal needs to travel the distance to the object, bounce off the object, and then travel the distance back to the receiver. So, distance becomes a factor.Because infrared receivers amplify the signal to improve detection, electrical noise generated from the oscillator can leak into the receiver and trigger a false detection. This isn't a problem for VCRs or most consumer devices as they tend to contain either a transmitter (remote control) or a receiver (CD player), but not both. Therefore, robot transmitter and receiver circuits must be carefully designed and positioned apart to be useful. Robots that chase electrical ghosts, spin in place, or jerk sporadically are initially amusing, but eventually frustrating. The lower the power of the circuit, the more likely it will be lower in noise. Also, liberal use of decoupling capacitors and metal shielding helps a lot. Greater distance between the circuits makes an enormous difference.
The oscillator will be used to generate a square wave at a desired frequency. The wave is fed into a transistor that drives an infrared LED on and off very rapidly. Because the emissions are infrared and very fast, neither is visible to the human eye. Inexpensive infrared receiver chips are available at 36 kHz, 38 kHz, and 40 kHz. The receivers are sensitive to oscillations several kilohertz to either side, although reception distance improves with a better signal to start with. If used for object detection, the signal needs to travel the distance to the object, bounce off the object, and then travel the distance back to the receiver. So, distance becomes a factor.Because infrared receivers amplify the signal to improve detection, electrical noise generated from the oscillator can leak into the receiver and trigger a false detection. This isn't a problem for VCRs or most consumer devices as they tend to contain either a transmitter (remote control) or a receiver (CD player), but not both. Therefore, robot transmitter and receiver circuits must be carefully designed and positioned apart to be useful. Robots that chase electrical ghosts, spin in place, or jerk sporadically are initially amusing, but eventually frustrating. The lower the power of the circuit, the more likely it will be lower in noise. Also, liberal use of decoupling capacitors and metal shielding helps a lot. Greater distance between the circuits makes an enormous difference.
The Popular 555
The 555 IC is an extremely popular timer. The low-power CMOS versions (TLC555, LMC555, and ICM7555) use less power than the older (555, NE555, LM555) versions and don't require a capacitor on the control pin. Although pin and functionally compatible, the component values differ between the low-power CMOS and older versions.
The 555 IC is an extremely popular timer. The low-power CMOS versions (TLC555, LMC555, and ICM7555) use less power than the older (555, NE555, LM555) versions and don't require a capacitor on the control pin. Although pin and functionally compatible, the component values differ between the low-power CMOS and older versions.
we can make a easy blog and join in google
0
online job गर्ने मित्रहरु लाई सुबर्ण अवसर । अब आफ्नो account लाई GOOGLE मा adsense गर्नुस अनि आफ्नो ब्लोग या साईट मा हुने प्रतेक क्लिक को फाइदा उठाउनुहोस् । अनि google बाहेक पनि त्यस्तो अरु धेरै लिन्क हरु छन । अनि हुन सक्छन् जुन तपाई लाई थाहा नभएको हुन सक्छ अनि या तपाई लाई थाहा भएको मलाई पनि थहा नहुन सक्छ । त्यसैले तपाई हरुले यहा त्यो लिन्क हरु बाढ्न सक्नु हुन्छ अनि लिन पनि । तपाई को लिन्क पोस्ट गर्न कमेन्ट बोक्स को प्रयोग गर्न सक्नु हुन्छ । ।
world without engineers
0Basic Electronics
0
INTRODUCTION
We are living in an age of Information Technology. Electronics is at the very foundation of the Information and Computer Age. The giant strides that we have made in the areas of Communications and Computers are possible only because of the great successes that we have achieved in the field of Electronics.
It is sometimes unbelievable, how many electronics gadgets that we carry these days in our person –Digital Wrist-watch, Calculator, Cell-phone, Digital Diary or a PDA, Digital Camera or a Video camera, etc.
The different types of Electronic equipments that has invaded our offices and homes these days is also mind boggling. Many things we use at home and office are “remote controlled”, for example, Television (TV), Air-Conditioners, Audio equipment, Telephone, etc. It is almost close to “magic” how even a child, now-a-days, can switch channels, or increase decrease the volume of sound in a TV at home by just clicking on a few buttons sitting at the comfort of a sofa away from the Television apparently without any physical wiring or connection!
Again, we are astonished, how we are able to talk to our near and dear living several thousands of kilometers away, from wherever we are, at home, office, on the road in a car, or in a classroom –by just clicking a few n umbers on our palm sized cellular phones!
Electronics has made deep impact in several vital areas such as health care, medical diagnosis and treatment, Air and space travels, Automobiles, etc. In short, the technological developments of several countries of the globe are directly related to their strengths in electronics design, manufacture, products and services. It appears as though we have to add inevitably an “E” to the three “R”s, namely, Reading, writing, and arithmetic, to declare a Man or Woman to be “literate”! Needless to add that the “E” here means “Electronics”! Thus Electronics has become surely a “Basic Science”. It is no more an “applied science”. Just as we teach physics, chemistry, biology and mathematics in our schools, it is high time we start teaching our children at school, Electronics as a separate subject by itself. This brings us face to face to an important question: How to teach the basic concepts of such an important subject like Electronics most effectively? If one wants to gain a good understanding of electronics, he or she should build circuits and test them independently. For this one should acquire a practical knowledge of the characteristics of different devices and in constructing the various circuits. Let us try to learn such skills by the proven scheme of “LEARNING BY DOING”. An old Chinese Proverb says: I Read -I Forget I See -I Remember I Do -I Understand There is only one way to learn to do anything: JUST DO IT!
LEARNING BY DOING
That is the way we all of us have learnt even as a child-to talk, walk, ride a cycle, etc. Many arts and special skills like dancing, singing swimming, and martial arts are all learnt by going to an expert or a teacher who makes us learn by doing rather than by listening to lectures or reading books. Why “learning by doing” is so important? Because, while doing we tend to fail and failures are very important in the learning process. Once we fail we start analyzing what went wrong. Thus at the point of failure a profound learning takes place. That is why people say: FAILURES ARE STEPPING STONES TO SUCCESS! In order to master the basic principles of electronics one has to study about the different components, circuits and measuring instruments used in electronics. There are two types of components that we come across namely Active and Passive components. Resistors, Capacitors, etc., are known as passive components because they can only attenuate the electrical voltage and signals and cannot amplify. Whereas devices like transistors, operational amplifier (Op Amp) can amplify or increase the amplitude and energy associated with the signals. Hence the transistors and OpAmp come under active devices. These components can be combined in different configurations by interconnecting them with conducting wires to build different useful Electronic circuits. We would here study about rectifiers, amplifiers, Oscillators, etc., under the category of circuits. Apart from the components and circuits we must also have familiarity on the principle of operations and usefulness of Some of the essential electronic measuring instruments such as digital millimeters, regulated power supplies, Function generators, oscilloscopes, etc., These help us in trouble shooting the circuits and identify the faulty components Whenever the circuits that we build do not work as expected. The diagram below gives in a nut shell the above ideas in the form of a flow diagram.
As a prerequisite for this course on basic Electronics, knowledge of general principles of electricity & magnetism is assumed. We will attempt here to learn Basic principles of electronics by the scheme “Learning by Doing”. In this web based course, the principles of operation of the different electronic devices, measuring instruments and circuits will be discussed and a set of simulated demonstration experiments are included wherever possible for the learner to perform these simple experiments on his/her own and learn the concepts by “doing.” This will enable the learner to gain greater confidence at the end in the principles and working of electronic devices and circuits. Before proceeding further, it is important to understand how the different circuits can be built and tested.Invariably a “bread-board” is used in a laboratory for constructing the different circuits and testing them. This is very useful since here, we do not have to solder the different components. Soldering, as you know can be very time consuming. Further, we can reuse the components again and again, since they are not cut and soldered.
The breadboard contains a number of metal clips aligned beneath the array of holes so that when we insert the lead of a component (say, resistor) inside a hole, the clip grips the lead tightly. Observe the figure. Fig (a) shows a metal clip before a component inserted, while Fig (b) shows after the lead inserted. Fig(c) shows a clip which is beneath an array of 5-holes. All the five holes correspond to one node since all of them are connected together electrically by the metal clip. That means up to 5 wires can be connected to this single node.
INTRODUCTION How to check the breadboard for this arrangement of connectivity below. We can do that simply by using a Digital Multi meter (DMM) and a couple f wires. Insert the wires into the two holes between which you want to heck the electrical continuity. Use the DMM in resistance mode and connect the two probes of the DMM to two strips of wires. If the resistance shown is Zero the they are connected. If the DMM reads high resistance then the two points are disconnected electrically (infinite resistance or open).
DIGITAL MULTI METER A Multi meter is indeed a multiple meter. It a measure dc and ac voltages, currents and in addition resistances! In some recent DMMs we can measure even frequency, capacitance, etc. Two long probes are used to connect the DMM to a circuit during a measurement. The central dial knob is rotated to choose the parameter we wish to measure. When not in use we keep the knob in OFF position. (See figure).
POWER SUPPLY
For performing experiments we need a Power supply which can provide the necessary power to activate the Circuits. The power supply we will be using here has the following outputs:
1.0 to 30 V variables DC Voltage, 1A max.
The voltage can be read on a digital display panel.
2.-15 _ 0 _ +15 Dual supply, 1.5 A max.
3.5V Fixed Dc Voltage output, 3A max.
we can use in all place
0
You can connect this circuit to any of your home application (Lamp, Fan, Radio, etc.) to make the application turn on/off from a TV, VCD or DVD remote control. The circuit can be activated from up to 10 meters... and we can make two ways switch from this circuit also.
It has three terminals in output side. Where one is use the in lode or line and two points is use in two way switch with parallel. Hope you can join the load easily in two way switch.
100 watt inverter circuit
0
यदी तपाई आफै इन्भर्टर को सर्किट पनि बनाउन चाहनुहुन्छ भने चाही यो सर्किट सबै भन्दा उपयोगी पनि छ अनि सस्तो पनि । यो १०० वाट को इन्भर्टर हो । जस्को सहायता ले तपाईहरु CFL बत्ती १० ओटा एकै पटक बाल्न सक्नु हुनेछ । यो एउटा इन्भर्टर को सर्किट मात्र हो त्यसैले बाकी आवस्यक सामान तपाईले click here हेर्न सक्नु हुनेछ ।
electronics
0
आज कल सबै नेपालिहरु एकै समस्या बाट ग्रसित हुनुहुन्छ । त्यो हो आम नेपाली ले महसुष गरेको कुरा लोड सेडिंग । हजुर यो समस्याले सम्पुर्ण नेपाली तर्सित हुनुहुन्छ । सायद म मद्दत गर्न सक्छु की ? ? ? ??
२०६५ साल को लोड सेडिंग ले त मलाई फाइदा नै गरायो !! अब यो वर्ष के हुन्छ हेरम । । तपाईहरु अचम्म हुनु भयो होला । मैले केही गरेको होइन, मात्र मेरो साथी भाई र आफन्तहरु को घर मा इन्भटर बेचेको हो । । तर म यो बर्ष तपाईहरु माझ पनि यो कुरा बाढ्न चाहदै छु । । हजुर म तपाई लाई इन्भटर कसरी बनाउने भन्ने बारे सिकाउछु । । तपाई लाई थाहा छ ? मैले इन्भटर बेच्नु भन्दा पहिले इन्भटर बनाउन आउदैन थियो तर पनि बेचेको थिय । अब भन्नु होला बेच्न त सबैले पनि सक्छ , तर त्यो समय मैले बनाएर नै बेचेको थिय । अब तपाई भन्नु होला के कुरा गरेको बनाउन आउदैन पनि भन्नु छ अनि बनाएको पनि कुरा गर्छ !!! हजुर बनाएको !! विस्वास लागेन ? ? तपाई हरु पनि बनाउन सक्नु हुन्छ, अनि आफै ले बनाउदा बजार बाट किन्दा भन्दा ५०% प्रतिसत पैसा बचत हुन्छ । यानेकी रु. १५०० मा नै बनौन सक्नु हुन्छ । । यदी बजार बाट किन्नु भयो भने घटी मा रु. ३००० मा पाउनुहुन्छ । त्यसले अब आफै कोसिष गर्ने पालो हो आउदैन भनेर मैले पनि हात बाधेर बसेको भए आज हजुर लाई सिकाउन सक्ने अवस्ता मा हुने थिइन होला । । ।
त्यसैले आफ्नो लागी मात्र भए पनि पैसा बचाउनुस । ३००० हजार को इन्भर्टर १५०० मा बनाउन सक्ने भए पछी किन नगर्ने ? ? ? म छु नि ........ कुनै समस्या आएको खण्ड मा कल पनि गर्न सक्नु हुनेछ ९८०३००३९८४ प्रदिप । इन्वर्टर कसरी बनाउने
1
आज कल सबै नेपालिहरु एकै समस्या बाट ग्रसित हुनुहुन्छ । त्यो हो आम नेपाली ले महसुष गरेको कुरा लोड सेडिंग । हजुर यो समस्याले सम्पुर्ण नेपाली तर्सित हुनुहुन्छ । सायद म मद्दत गर्न सक्छु की ? ? ? ?
२०६५ साल को लोड सेडिंग ले त मलाई फाइदा नै गरायो !! अब यो वर्ष के हुन्छ हेरम । । तपाईहरु अचम्म हुनु भयो होला । मैले केही गरेको होइन, मात्र मेरो साथी भाई र आफन्तहरु को घर मा इन्भटर बेचेको हो । । तर म यो बर्ष तपाईहरु माझ पनि यो कुरा बाढ्न चाहदै छु । । हजुर म तपाई लाई इन्भटर कसरी बनाउने भन्ने बारे सिकाउछु । । तपाई लाई थाहा छ ? मैले इन्भटर बेच्नु भन्दा पहिले इन्भटर बनाउन आउदैन थियो तर पनि बेचेको थिय । अब भन्नु होला बेच्न त सबैले पनि सक्छ , तर त्यो समय मैले बनाएर नै बेचेको थिय । अब तपाई भन्नु होला के कुरा गरेको बनाउन आउदैन पनि भन्नु छ अनि बनाएको पनि कुरा गर्छ !!! हजुर बनाएको !! विस्वास लागेन ? ? तपाई हरु पनि बनाउन सक्नु हुन्छ, अनि आफै ले बनाउदा बजार बाट किन्दा भन्दा ५०% प्रतिसत पैसा बचत हुन्छ । यानेकी रु. १५०० मा नै बनौन सक्नु हुन्छ । । यदी बजार बाट किन्नु भयो भने घटी मा रु. ३००० मा पाउनुहुन्छ । त्यसले अब आफै कोसिष गर्ने पालो हो आउदैन भनेर मैले पनि हात बाधेर बसेको भए आज हजुर लाई सिकाउन सक्ने अवस्ता मा हुने थिइन होला । । ।
त्यसैले आफ्नो लागी मात्र भए पनि पैसा बचाउनुस । ३००० हजार को इन्भर्टर १५०० मा बनाउन सक्ने भए पछी किन नगर्ने ? ? ? म छु नि ........ कुनै समस्या आएको खण्ड मा कल पनि गर्न सक्नु हुनेछ ९८०३००३९८४ प्रदिप ।
इन्भर्टर दुई तरिका ले बनाउन सकिन्छ । अनि UPS इन्भर्टर को बारेमा भन्दा पनि घर हरु मा प्रयोग गर्ने तर सजिलै बनाउन सकिने तरिका म भन्दै छु । इन्भर्टरको पनि क्षमता हुन्छ । यसलाई वाट मा नापिन्छ । अनि तपाई कती वाट को इन्भर्टर वनाउन चाहनु हुन्छ ? तेस्को इन्भर्टर बनाउन को लागी तपाइले सजिलै संग बजार मा सामान पाउन सक्नु हुनेछ । चाहिने सामान निम्न छन् :-
१ इन्भर्टर किट ( तपाई आवव्सकता अनुसार )
२ ट्रान्स्फर्मर २ एम्पियर , १२ भोल्ट्, ०-१२ ( १ ओटा )
३ क्यापासिटोर २५ भोल्ट २२०० माइक्रो फ्यारेड ( १ ओटा )
४ डायोड ४००७ नम्बर ( ४ ओटा )
५ लिड (LED) रातो रंगको ( १ ओटा )
६ रेजिस्टर १०० ओहम
७ स्विच
१ इन्भर्टर किट ( तपाई आवव्सकता अनुसार )
२ ट्रान्स्फर्मर २ एम्पियर , १२ भोल्ट्, ०-१२ ( १ ओटा )
३ क्यापासिटोर २५ भोल्ट २२०० माइक्रो फ्यारेड ( १ ओटा )
४ डायोड ४००७ नम्बर ( ४ ओटा )
५ लिड (LED) रातो रंगको ( १ ओटा )
६ रेजिस्टर १०० ओहम
७ स्विच
तपाई कुनै सामान किन्नु अघी तपाइ कन्फियुज हुनुहुन्छ भने फोन गर्न सक्नु हुनेछ ९८०३५५३९८४ प्रदिप ।